场景几何结构
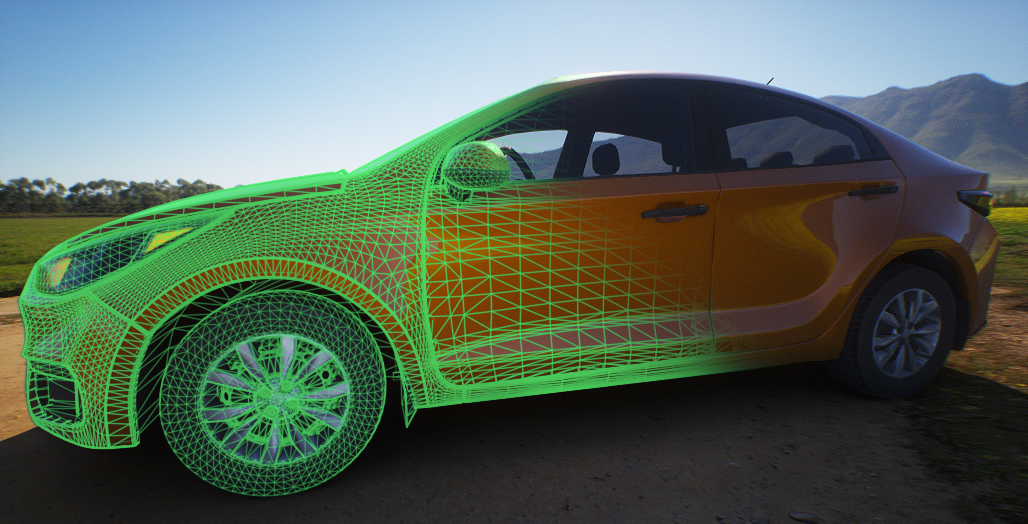

In a virtual world, a three-dimensional object is typically represented as a collection of points with coordinates, edges connecting these points, and faces stretching across these edges. Let's go through all these components.在虚拟世界中,一个三维物体通常表示为具有坐标的点的集合、连接这些点的边以及跨越这些边的面。让我们逐一了解这些组成部分。
A point, also known as a vertex, is the foundation. Without points there will be nothing, neither a cube, nor even a line. Points, however, can exist on their own and have their own coordinates.顶点(Vertex):具有坐标的空间点,是几何基础元素。没有顶点就无法构建任何图形,甚至无法形成一条线段。然而,点可以独立存在并拥有自己的坐标。
An edge is a connection of two points, or a segment in three-dimensional space. It is defined by the points it connects and the line itself.边(Edge):连接两个顶点的线段,在三维空间中定义几何轮廓。它由所连接的点及其本身所在的线定义。
Percieving only points and edges is not an easy task, therefore, edges form a frame across which faces are stretched, which allow us to see the object painted in any color or using materials that determine its appearance.仅感知点和边并非易事,因此边构成了一个框架,在其上拉伸出面,这使我们能够看到被涂成任何颜色或使用决定其外观的材质的物体。
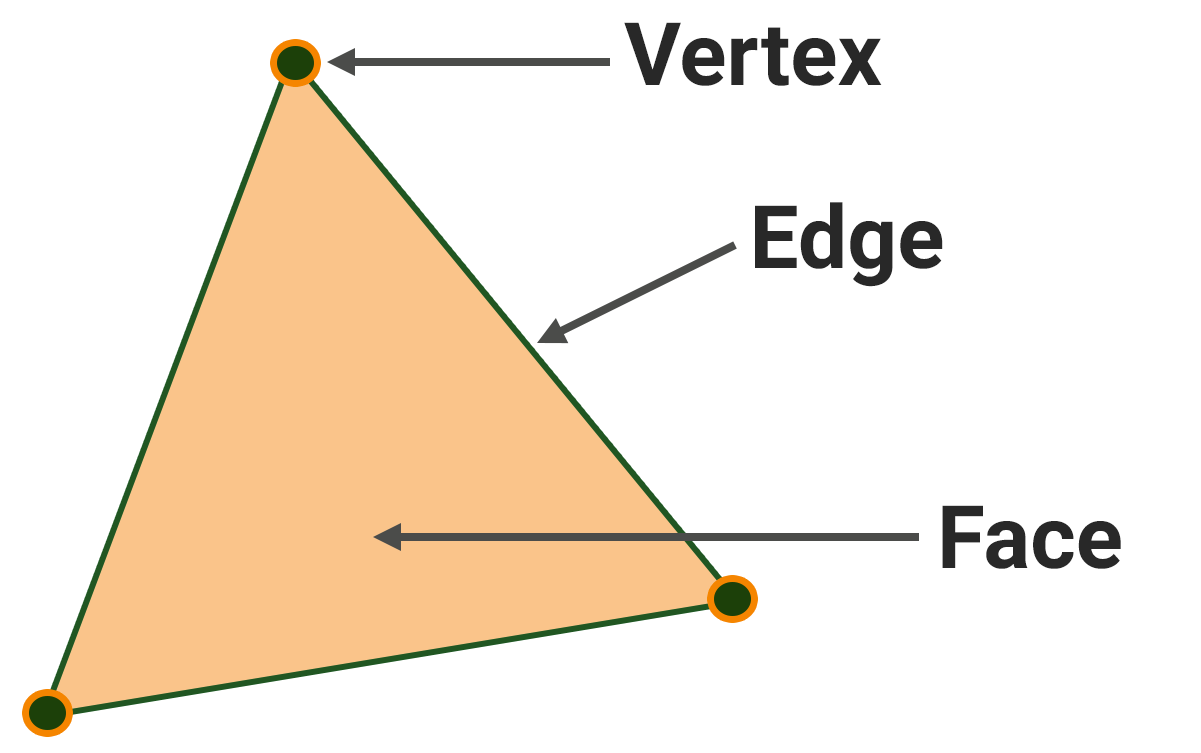
So, a face is stretched across a closed contour of edges (i.e. its starting point coincides with the end point). The minimum number of face edges is three, if it's less, then we'll have an edge. An important notice here: a face with 3 edges cannot be bent — no matter which vertex we pull, all its edges will always lie in one plane. This is crucial for computer calculations, so a face stretched across a closed contour of 3 edges — a triangle — is an important element of geometry, along with a point and an edge. A triangle is characterized by the coordinates of its vertices, the edges, and the normal.因此,一个面被拉伸在边的闭合轮廓上(即其起点与终点重合)。面的最小边数是三条,如果少于三条,我们就只有一条边。这里需要注意:具有3条边的面不能被弯曲,无论我们拉哪个顶点,它的所有边都将始终位于同一平面上。这对计算机计算至关重要,因此跨越3条边闭合轮廓的面:三角形,是与点和边同等重要的几何元素。三角形的特征是其顶点的坐标、边和法线。
The normal is a computer characteristic needed to calculate lighting. A triangle has two surfaces - an outer surface facing outward from the object and an inner surface facing inward. Light falls on the surface of the triangle from the outer side, and the normal vector is the vector going outwards from the triangle at the right angle to its surface. The inner sides of faces are often not drawn, and if you look at a face from inside the object, it won't be visible.法线是计算光照所需的计算机特性。三角形有两个表面:一个从物体向外朝外的外表面和一个向内朝内的内表面。光线从外侧照射到三角形的表面上,法线向量是从三角形表面垂直向外指的向量。面的内侧通常不被绘制,如果你从物体内部看一个面,它将不可见。
All faces having more than three edges, and any surface in general, can be approximated with triangles to a sufficient degree of accuracy. The word sufficient in this case refers to the minimum number of triangles required to achieve an acceptable appearance of the surface, as adding more triangles can increase the load on the renderer (while reducing it is one of the crucial tasks). This process of dividing a surface into triangles is known as triangulation, while increasing the level of detail on an already triangulated surface is called tessellation. Graphics APIs such as Vulkan and DirectX, as well as graphics cards, exclusively operate with triangles.所有具有多于三条边的面,以及任何表面,都可以用三角形以足够的精度近似表示。这里的"足够"指的是达到可接受的表面外观所需的最少三角形数量,因为增加三角形数量会增加渲染器的负载(而减少负载是关键任务之一)。将表面分割成三角形的过程称为三角剖分,而在已经三角化的表面上增加细节层次称为曲面细分。图形API如Vulkan和DirectX以及显卡都专门处理三角形。
Of course, while creating a model, no one manually breaks all its faces into triangles — there are algorithms available specifically for this purpose. Thus you can create faces as polygons, which are sets of triangles lying in one plane and touching each other with edges.当然,在创建模型时,没有人会手动将所有面分割成三角形:有专门用于此目的的算法可用。因此,你可以创建作为多边形的面,这些面是位于同一平面并通过边相互接触的三角形集合。

Closed frame of edges边的闭合框架
|
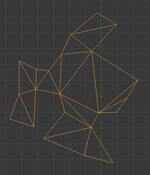
Frame triangulation框架的三角剖分
|
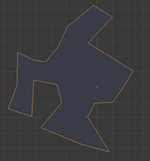
Polygon in the frame框架中的多边形
|
By connecting edges (polygons or triangles) lying in different planes, we get what is called an object.通过连接位于不同平面上的边(多边形或三角形),我们得到了所谓的物体。
So, the fundamental geometric concepts in 3D are point, edge, triangle (the elementary ones), and polygon (the derivative one). And an object is just a container for geometric elements.因此,3D中的基本几何概念是点、边、三角形(基本元素)和多边形(派生元素)。而物体只是几何元素的容器。
Mesh and Its Surfaces网格及其表面#
A mesh is a set of vertices, edges, and triangular faces (organized into polygons) that define the geometry of an object. Meshes include one or more groups of polygons, which are called surfaces.网格是由顶点、边和三角面(组织成多边形)组成的集合,用于定义物体的几何形状。网格包含一个或多个多边形组,这些组被称为表面。
A surface is a subset of the object geometry (i.e. a mesh) that does not overlap other subsets. Each surface can be assigned its own material or property. In addition, surfaces within a mesh can be organized into a hierarchy, and each surface can be switched on or off independently of the others — this can also be used for switching between levels of detail (LOD), we'll discuss this later. Thus, a surface can represent:表面(surface)是物体几何体(即网格)中不与其他子集重叠的子集。每个表面都可以分配自己的材质或属性。此外,网格中的表面可以组织成层次结构,每个表面可以独立于其他表面开启或关闭,这也可以用于在不同细节级别(LOD)之间切换,我们稍后会讨论这一点。因此,一个表面可以表示:
- Part of the object to which an individual material is assigned (for example, a magnifying glass may have two surfaces — a metal ring with a handle and the glass itself).分配了单独材质的物体部分(例如,放大镜可能有两个表面:带手柄的金属环和玻璃本身)。
- One of the levels of detail (LOD), including LODs for reflections and shadows. In this case, the surfaces represent the same object or its part in a more or less detailed form (high- and low-polygonal meshes). Each surface has a set of properties that allow defining the visibility distance (the farther away from the camera, the less detailed surface is required to be rendered).细节级别(LOD)之一,包括用于反射和阴影的LOD。在这种情况下,表面以更详细或更简化的形式表示同一物体或其部分(高多边形和低多边形网格)。每个表面都有一组属性,可用于定义可见距离(离摄像机越远,需要渲染的表面细节越少)。
This is why one mesh can have many surfaces. The quadcopter mesh in the picture below consists of four sufraces: moving part of the frame (arms and protection), body, small parts, and landing gear and propellers.这就是为什么一个网格可以有许多表面。下图中的四轴飞行器网格由四个表面组成:框架的活动部分(臂和保护装置)、机身、小零件,以及起落架和螺旋桨。
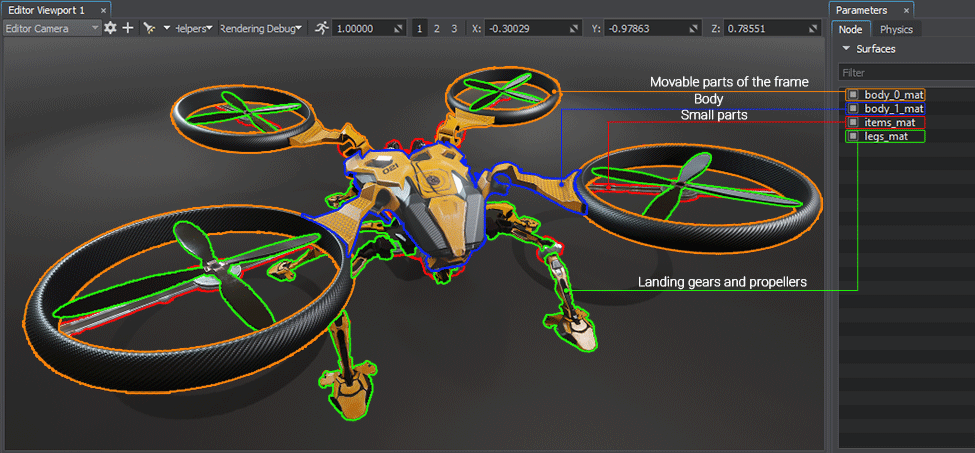
The most commonly used object is Static Mesh — it can be moved, rotated and scaled, but the geometry itself cannot be changed: the positions of their vertices are unchanged.最常用的对象是静态网格(Static Mesh),它可以移动、旋转和缩放,但其几何形状本身无法更改:其顶点的位置保持不变。
Object models are created in third-party graphics programs (such as 3ds Max, Maya, etc.) and can be imported through UnigineEditor — their geometry is converted into UNIGINE's own format (*.mesh). In UNIGINE, meshes have 32-bit precision, so we recommend placing meshes at the origin before exporting them from third-party graphics programs, and then placing the mesh in UnigineEditor.物体模型是在第三方图形程序(如3ds Max、Maya等)中创建的,可以通过UnigineEditor导入,其几何形状会被转换为UNIGINE自有格式(*.mesh)。在UNIGINE中,网格具有32位精度,因此我们建议在从第三方图形程序导出之前将网格放置在原点,然后在UnigineEditor中放置网格。
In 3D modeling, surfaces are rendered as individual elements that require their own DIP rendering call. To render a surface, a material must be assigned to determine its appearance, such as whether it will be matte or glossy and have a wood or brick texture. Textures are used to set the color and texture of the surface at each point and are overlaid onto the model's surface using a UV map or map stored within the model (we'll review materials and textures in more detail later). This map converts (X,Y,Z) space coordinates to UV space coordinates, with U and V coordinates taking values from 0 to 1. Modern video cards consider the UV transformation within a single triangle to be affine, requiring only U and V coordinates for each vertex. So, it is up to 3D modelers to decide how to connect the triangles to each other, and creating a successful unwrapping is an indicator of their skill level.在3D建模中,表面是作为需要独立DIP渲染调用的单独元素进行渲染的。要渲染一个表面,必须为其分配材质以决定其外观,比如是哑光还是高光、具有木质还是砖纹纹理。纹理用于设置表面每个点的颜色和纹理,并通过UV贴图或存储在模型内部的贴图覆盖到模型表面(我们稍后将更详细讨论材质和纹理)。这种贴图将(X,Y,Z)空间坐标转换为UV空间坐标,U和V坐标的取值范围是0到1。现代显卡认为单个三角形内的UV变换是仿射变换,只需要每个顶点的U和V坐标。因此,如何将三角形相互连接取决于3D建模师,而创建成功的展开图是他们技能水平的体现。
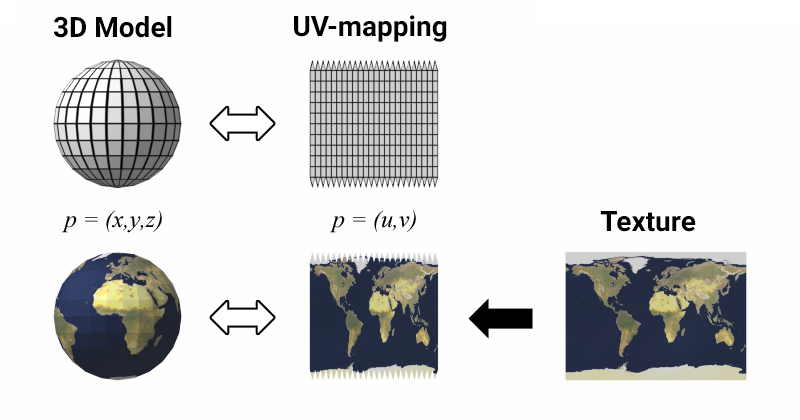
There are several mapping quality parameters, which may be contradictory:存在几个可能相互矛盾的贴图质量参数:
- Maximizing the use of texture space. Compact layout is necessary for efficient memory use and higher texture detail on the model. However, keep in mind that a certain allowance is required at the edges of the unwrapping to generate smaller textures.最大化利用纹理空间。紧凑的布局对于高效利用内存和提高模型纹理细节是必要的。但要注意,在展开图的边缘需要留出一定余量以生成更小的纹理。
- Avoiding areas with excessive or insufficient detail.避免细节过多或不足的区域。
- Avoiding areas with excessive geometry distortions.避免几何变形过大的区域。
- Maintaining the viewing angles from which an object is usually drawn or photographed to simplify the texture artist's work.保持物体通常被绘制或拍摄的视角,以简化纹理艺术家的工作。
- Effectively locating seams — the lines that correspond one edge but are positioned in different areas of the texture. Seams are desirable if a surface has a natural interruption (clothing seams, edges, joints, etc.) and should be avoided if there is none.有效定位接缝:对应同一条边但位于纹理不同区域的线条。如果表面有自然中断(衣服接缝、边缘、连接处等),接缝是可取的;如果没有则应避免。
- For partially symmetrical objects: combining of symmetrical and asymmetrical parts of the layout. Symmetry increases texture detail and simplifies the artist's work; asymmetrical details juice up the object.对于部分对称物体:结合对称和非对称的布局部分。对称性可提高纹理细节并简化艺术家工作;非对称细节则使物体更生动。
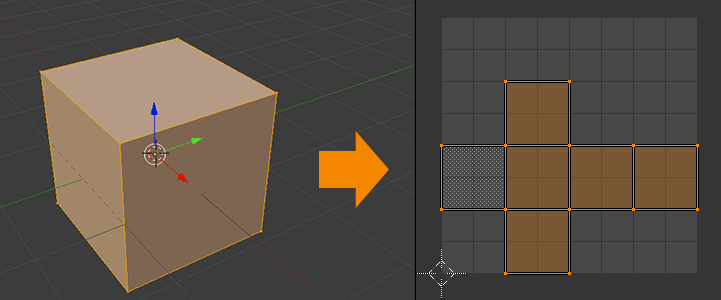
The unwrapping can be done either manually or automatically, and many tools (Maya, Blender, 3D Max, and others) offer an auto unwrapping feature. UNIGINE has this functionality too, and you can generate a UV unwrapping at the model import, which can be used for lighting maps or for drawing directly on the object.展开可以手动或自动完成,许多工具(Maya、Blender、3D Max等)都提供自动展开功能。UNIGINE也具备此功能,你可以在模型导入时生成UV展开图,用于光照贴图或直接在物体上绘制。
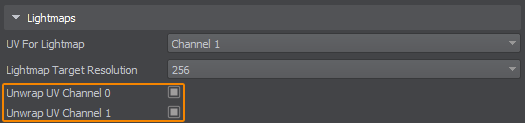
Each surface in UNIGINE has 2 UV channels. You can specify in the material settings which UV channel to use. For example: the first UV channel can be used for tiling and detail textures, and the second for light maps.在UNIGINE中,每个表面有2个UV通道。你可以在材质设置中指定使用哪个UV通道。例如:第一个UV通道可用于平铺和细节纹理,第二个用于光照贴图。
本页面上的信息适用于 UNIGINE 2.20 SDK.
