光照系统
In computer graphics, it is lighting what makes a scene look realistic. Properly installed and adjusted lighting can enhance a very mediocre scene, and by contrast, the impression of a well-modeled scene can be ruined by placing light sources carelessly, which can also negatively affect performance. Proper lighting determines the overall atmosphere of the picture displayed to the user. Light can help you to convey mood, emphasize the advantages and hide the flaws.在计算机图形学中,正是光照使场景呈现真实感。恰当设置的光照能显著提升普通场景的品质,反之,随意放置的光源不仅会破坏精心建模场景的观感,还会影响性能表现。合理的光照决定了呈现给用户的整体画面氛围,能有效传递情绪、突出优点并掩饰缺陷。
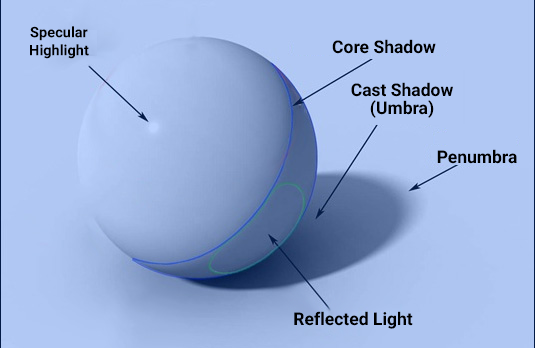
Objects in the scene won't look flat if they have light and shade upon them, that is, light is distributed on the object's shape depending on the position of its various surfaces in relation to the light source. To make objects look three-dimensional, they must have light, highlight, halftone, and the most shaded part of the surface — core of shadow. The latter is always illuminated to some degree by light reflected from other objects (reflected light). Finally, objects themselves cast a shadow on neighboring objects, which is usually darker than their own shadow. Only the right balance of all these light phases can convey the object's volume with the utmost plausibility.当物体表面具有明暗变化时(即光线根据各表面相对于光源的位置进行分布),场景中的物体就不会显得扁平。要使物体呈现立体感,必须包含以下光相:直接受光部、高光区、中间调,以及表面阴影核心区。阴影核心总会受到其他物体反射光的些许影响(反射光)。最终,物体还会在邻近物体上投射阴影(通常比自身阴影更暗)。只有这些光相的精准平衡才能最大程度真实地表现物体体积。
In computer graphics lighting is divided into two categories:计算机图形学将光照分为两类:
- Direct – rays of light come from the light source directly onto the surface.直接光照:光线从光源直接照射物体表面
- Reflected – rays are reflected from the surface, scattered, and form a soft fill light.间接光照:光线经表面反射、散射后形成的柔和填充光
There are many methods for calculating reflected illumination, and one of the best known (and probably the most 'honest') is Global Illumination (GI).间接光照计算有多种方法,其中最著名(或许也最"精确")的是全局光照(GI,Global Illumination)。
A light source emits rays made up of photons — particles that carry information about the light color and brightness. Falling on a surface, the rays illuminate it, but the photons lose some of their energy, causing the ray color and brightness to change. Then the rays are reflected (photons bounce back) and fall on the next surface, losing some more energy. The number of such "bounces" is determined by the rendering settings.光源发射由光子组成的光线——这些粒子携带光色与亮度信息。当光线照射表面时,光子会损失部分能量,导致光线颜色和亮度改变。反射光线(光子反弹)会继续照射其他表面,并持续损失能量。这种"反弹"次数由渲染设置决定。
In addition to reflected light, there is also Ambient Occlusion (AO). This is the effect of shading in corners, cracks, and narrow openings. Imagine that a beam of light flies into the corner of the room, is reflected several times from both walls, and gradually fades. The farther is the corner into the room, the less light gets there.除间接光外,还有环境光遮蔽(AO,Ambient Occlusion)效应——即角落、裂缝等狭窄区域的阴影效果。设想一束光射入房间角落,经墙面多次反射后逐渐衰减。越深的角落接收的光线越少。
 |
 |
| Without the AO texture无AO纹理 | With the AO texture有AO纹理 |
As a rule, Ambient Occlusion is used to artistically emphasize the shading effect — in real life, light rays do not lose energy so quickly that the corners of the room become as dark as they sometimes are in games. If the engine supports physically correct lighting, then it can calculate the rate of energy loss by the light beam on its own, and you don't have to create a specific Ambient Occlusion texture. But having this texture would help you to emphasize the relief of the object drawn on the main texture (otherwise the material may look more flat). The AO texture is a black-and-white texture that stores shadows cast from diffuse lighting.通常环境光遮蔽用于艺术化强调阴影效果;现实中光线衰减不会像游戏中那样剧烈。若引擎支持物理精确光照,可自动计算光线能量衰减率,此时无需专门制作AO纹理。但使用AO纹理能强化主纹理表现的物体凹凸感(否则材质会显得较平)。AO纹理是存储漫反射阴影的黑白贴图。
本页面上的信息适用于 UNIGINE 2.20 SDK.
