碰撞检测与射线投射
In the real world, bodies usually don't move without constraints and obstacles, and the same goes for virtual worlds. For correct processing of the situation when the body meets an obstacle, collision detection is used.在现实世界中,物体通常不会无约束地移动而不遇到障碍,虚拟世界亦是如此。为了正确处理物体遇到障碍物的情况,需要使用碰撞检测技术。
Regardless of their implementation, collision detection algorithms usually operate with collision shapes that we have been talking about recently.无论具体实现方式如何,碰撞检测算法通常都基于我们最近讨论过的碰撞形状(Collision shapes)进行操作。
There are two types of collisions implemented in UNIGINE depending on the types of colliding objects:UNIGINE中实现了两种类型的碰撞,具体取决于碰撞对象的类型:
- Shape — Shape collision between two objects with physical properties assigned (having a body and at least one shape, both enabled). In this case, the contact points between the shapes are found.形状与形状碰撞(Shape — Shape)发生在两个具有物理属性的对象之间(拥有物理体和至少一个启用的形状)。这种情况下会计算形状之间的接触点。
- Shape — Surface collision between an object with physical properties assigned and a non-physical object (without physical representation). If the surface has the Collision flag set, it can also passively participate in physical interaction and prevent the physical object from going through. In this case, contact points between the shape and surface polygons are computed.形状与表面碰撞(Shape — Surface)发生在具有物理属性的对象与无物理属性有表面(surface)的对象(没有物理表示)之间。如果表面设置了Collision(碰撞)标志,它也可以被动参与物理交互并阻止物理对象穿透。这种情况下会计算形状与表面多边形之间的接触点。
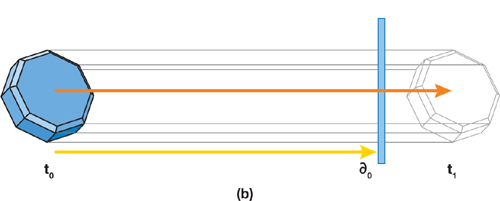
So, collision detection is enabled automatically for an object with a body and a collision shape, or when at least one of its surfaces has the Collision flag set.因此,当对象具有物理体和碰撞形状,或者当其至少一个表面设置了Collision(碰撞)标志时,碰撞检测会自动启用。
The algorithm for enabling/disabling collision detection is illustrated below:启用/禁用碰撞检测的算法如下图所示:
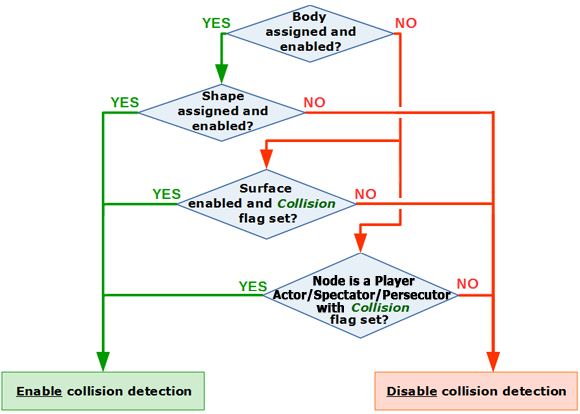
- Disabling physics simulation globally does not turn off collision detection.全局禁用物理模拟不会关闭碰撞检测功能。
- If the object has the body and shape assigned and enabled, the collision detection algorithms will use only the shape parameters, while the parameters of its surfaces will be ignored.如果对象分配并启用了物理体和形状,碰撞检测算法将仅使用形状参数,而忽略其表面参数。
Complex scenes may contain a lot of objects for which physics simulation is enabled, but not all of them need to interact with each other.复杂的场景可能包含大量启用了物理模拟的对象,但并非所有对象都需要相互交互。
For optimization purposes, you can use the Collision mask. It allows you to limit the number of objects that a physical object can collide with. Only surfaces and collision shapes with matching masks will collide.出于优化目的,你可以使用碰撞遮罩(Collision mask)。这可以限制物理对象能够与之碰撞的对象数量。只有具有匹配遮罩的表面和碰撞形状才会发生碰撞。
The Exclusion mask can be used to define shapes that should ignore each other.排除遮罩(Exclusion mask)可用于定义应相互忽略的形状。
The whole process is divided into the following stages and phases:整个过程分为以下阶段和环节:
- Collision Detection碰撞检测
- Collision Response碰撞响应
- Event Handlers Execution事件处理程序执行
Collision Detection碰撞检测#
During this phase, we find all collisions with all contact points and collect all necessary information. First, our pairs of objects that are positioned too far to collide are filtered. Then, all collisions along with contact points for all colliding bodies are found.在此环节中,我们会找出所有碰撞接触点并收集所有必要信息。首先过滤掉相距过远不可能碰撞的对象对。然后找出所有碰撞体之间的碰撞接触点。
So, here we collect all the data required to resolve collisions later — contact points coordinates, normals, depth of shapes penetration, relative velocity (between two bodies), relative friction and restitution.这里我们收集后续解决碰撞所需的所有数据——接触点坐标、法线、形状穿透深度、相对速度(两个物体间)、相对摩擦力和弹性系数。
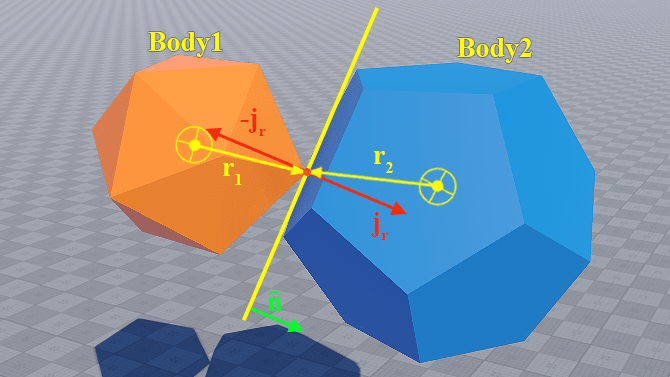
Collision Response碰撞响应#
So, we've got all the necessary information about collisions. Now we need to process this information to provide a realistic reaction. Collision response stands for simulation of the changes in the motion of two solid bodies after collision. UNIGINE uses an impulse-based reaction model. During response calculation, two parameters — the restitution and friction coefficients — are taken into account. These coefficients can be set for a shape as well as for a surface.我们已经获得了所有必要的碰撞信息。现在需要处理这些信息以提供真实的反应效果。碰撞响应是指模拟两个刚体碰撞后运动状态的变化。UNIGINE采用基于冲量的反应模型。在响应计算过程中会考虑两个参数——弹性系数和摩擦系数。这些系数既可以为形状设置,也可以为表面设置。
Event Handlers Execution事件处理程序执行#
At this stage, all user-defined physics event handlers are called. They are executed in certain physics-related events. These event handlers are mainly used for creation, destruction, or modification of other objects, such operations can only be performed in the main thread.在此阶段,会调用所有用户定义的物理事件处理程序。它们会在特定的物理相关事件中执行。这些事件处理程序主要用于创建、销毁或修改其他对象,此类操作只能在主线程中执行。
Discrete and Continuous Collision Detection离散与连续碰撞检测#
In UNIGINE, physics is simulated at its own frame rate that doesn’t depend on the rendering frame rate. As we discussed earlier, you can specify the number of cycles of physics simulation during one physics tick in the global settings.在UNIGINE中,物理模拟拥有独立于渲染帧率的专属帧率。如先前所述,你可在全局设置中指定单个物理帧内的物理模拟循环次数。
Basically, collisions are calculated each physics tick. This approach is called discrete collision detection. Such discretization improves performance and is accurate enough. However, when the frame rate is low, small, fast-moving objects are likely to teleport from one point to another instead of moving smoothly, so collisions are not detected.基础碰撞检测采用离散碰撞检测方式,即每个物理帧计算一次碰撞。这种离散化处理提升了性能且精度足够。但当帧率较低时,快速移动的小型物体可能出现"瞬移"现象而非平滑移动,导致碰撞未被检测。
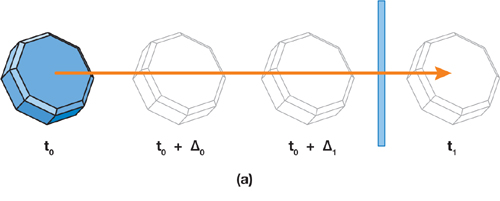
In continuous collision detection, the Engine calculates contact points the body will have (in the current physical frame) if it continues its current trajectory. These calculations are based on the velocity of the body and the radius of the collision shape. In other words, moving bodies are extruded along their trajectory, forming a volume used for collision detection at higher speeds.连续碰撞检测模式下,引擎会基于物体当前速度及碰撞形状半径,预计算物体在当前物理帧内沿运动轨迹将产生的接触点。换言之,运动物体沿轨迹被"拉伸"形成一个体积,用于高速状态下的碰撞检测。
Thus, contacts are checked not just once per frame but during the entire frame. This approach excludes missed collisions.因此,接触检测并非每帧仅执行一次,而是贯穿整个帧周期。这种方法可有效避免漏检。
Physics Intersections物理相交检测(Physics Intersections)#
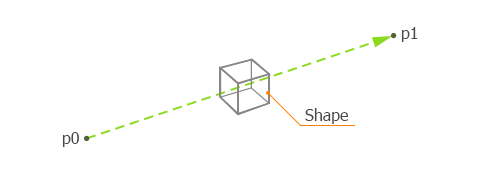
In some cases, you can use physics intersections for collision detection. Intersection detection lies at the heart of collision detection, but it is a particular case of ray intersection (ray casting).某些情况下可采用物理相交检测替代碰撞检测。相交检测本质上是碰撞检测的核心,但属于射线相交(ray casting)的特殊应用场景。
Intersection calculation is less expensive than collision calculation — a ray is cast from a certain point in a certain direction to find the first intersection with a surface or a collision shape.相交检测的计算开销低于完整碰撞检测:从特定点沿指定方向发射射线,寻找与表面或碰撞形状的首次相交点。
For example, calculation of collisions of car wheels with the ground takes time and decreases the frame rate. Instead, you can use the intersection of rays cast from the bottom of the car with the ground.例如,完整计算车轮与地面的碰撞会消耗大量时间并降低帧率。此时可采用从车底向下发射射线检测地面相交的替代方案。
And if you want to exclude some obstacles, you can use the Physics Intersection mask. Physics intersection is detected only if the Physics Intersection mask of the surface or shape matches the Intersection mask defined for the ray.若需排除特定障碍物,可使用Physics Intersection(物理相交)遮罩系统。仅当表面或形状的物理相交遮罩与射线定义的相交遮罩匹配时,才会触发物理相交检测。
本页面上的信息适用于 UNIGINE 2.20 SDK.
